Internet Governance Main
Investigating TLS blocking in India
A study into Transport Layer Security (TLS)-based blocking by three popular Indian ISPs: ACT Fibernet, Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio.
Towards Algorithmic Transparency
This policy brief examines the issue of transparency as a key ethical component in the development, deployment, and use of Artificial Intelligence.
Response to the ‘Call for Comments’ on The Santa Clara Principles on Transparency and Accountability
The Santa Clara Principles on Transparency and Accountability, proposed in 2018, provided a robust framework of transparency reporting for online companies dealing with user-generated content. In 2020, the framework underwent a period of consultation "to determine whether the Santa Clara Principles should be updated for the ever-changing content moderation landscape." In lieu of this, we presented our responses, which are in-line with our previous research and findings on transparency reporting of online companies, especially in context of the Indian digital space.
Remove misinformation, but be transparent please!
The Covid-19 pandemic has seen an extensive proliferation of misinformation and misleading information on the internet - which in turn has highlighted a heightened need for online intermediaries to promptly and effectively deploy its content removal mechanisms. This blogpost examines how this necessity may affect the best practices of transparency reporting and obligations of accountability that these online intermediaries owe to their users, and formulates recommendations to allow preservation of information regarding Covid-19 related content removal, for future research.
Donald Trump is attacking the social media giants; here’s what India should do differently
For a robust and rights-respecting public sphere, India needs to ensure that large social media platforms receive adequate protections, and are made more responsible to its users.
Cryptocurrencies in India get a second wind
An analysis of the Supreme Court judgment cryptocurrency judgment.
Guest Report: Bridging the Concerns with Recommending Aarogya Setu
Keywords: Aarogya Setu, Constitutionality, Digital Contact Tracing, Location Data, Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019, Exemptions, Personal Data, Sensitive Personal Data, Mosaic Theory, Surveillance, Privacy, Governing Law, Necessity, Intensity of Review, disparate Impact, Proportionality
Geo-economic impacts of the coronavirus: Global Supply Chains (Part I)
This two part blog post looks at the geo-economic impacts of the coronavirus by examining crucial impacts of developments in China. Part I looks at the impact of China's shutdown on global supply chains and part two, considers the implications for the future of 5G technology.
The debate over internet governance and cyber crimes: West vs the rest?
The post looks at the two models proposed for internet governance and the role of cyber crimes in shaping the debate. In this context, it will also critically analyze the Budapest Convention (the “convention”) and the recently proposed Russian Resolution (the “resolution”), and the strategies adopted in each to deal with the menace of cybercrimes. It will also briefly discuss India’s stances on these issues.
Freedom of Expression in India: Key Research and Findings
Over the last two years, CIS has carried out critical research on the issue of freedom of expression in India. We have continued our work on intermediary liability, as well as expanded our expertise to emerging areas, like online extreme speech. Researchers have also closely tracked developments around internet shutdowns, and the impact of social media and data on democratic processes in the country.
Essay: Watching Corona or Neighbours? - Introducing ‘Lateral Surveillance’ during COVID-19
Surveillance is already suspected to have become the ‘new normal’ considering the extensive amounts of money that is being invested by governments around the globe. The only way out of this pandemic is to take a humane approach to surveillance wherein the discriminatory tendencies of the people while spreading information about those infected are factored in to prevent excessive harm.
Rumours, Misinformation and Self-Verification of Facts in the Age of COVID-19
Efforts taken by the government or social media platforms can only be realised if an individual asks herself -- 'what can I do to verify this piece of information'?
Why should we care about takedown timeframes?
The issue of content takedown timeframe - the time period an intermediary is allotted to respond to a legal takedown order - has received considerably less attention in conversations about intermediary liability. This article examines the importance of framing an appropriate timeframe towards ensuring that speech online is not over-censored, and frames recommendations towards the same.
After the Lockdown
This post was first published in the Business Standard, on April 2, 2020.
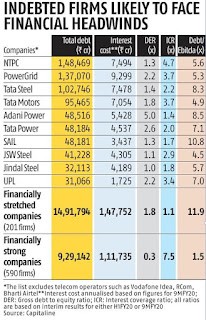
Source: Krishna Kant: "Coronavirus shutdown puts Rs 15-trillion debt at risk, to impact finances", BS, March 30, 2020:
For the longer term, a fundamental reconsideration for allocating resources is needed through coherent, orchestrated policy planning and support. What the government can do as a primary responsibility, besides ensuring law and order and security, is to develop our inadequate and unreliable infrastructure, including facilities and services that enable efficient production clusters, their integrated functioning, and skilling. For instance, Apple’s recent decision against moving iPhone production from China to India was reportedly because similar large facilities (factories of 250,000) are not feasible here, and second, our logistics are inadequate. Such considerations should be factored into our planning, although Apple may well have to revisit the very sustainability of the concept of outsize facilities that require the sort of repressive conditions prevailing in China. However, we need not aim for building unsustainable mega-factories. Instead, a more practical approach may be to plan for building agglomerations of smaller, sustainable units, that can aggregate their activity and output effectively and efficiently. Such developments could form the basis of numerous viable clusters, and where possible, capitalise on existing incipient clusters of activities. Such infrastructure needs to be extended to the countryside for agriculture and allied activities as well, so that productivity increases with a change from rain-fed, extensive cultivation to intensive practices, with more controlled conditions.
The automotive industry, the largest employer in manufacturing, provides an example for other sectors. It was a success story like telecom until recently, but is now floundering, partly because of inappropriate policies, despite its systematic efforts at incorporating collaborative planning and working with the government. It has achieved the remarkable transformation of moving from BS-IV to BS-VI emission regulations in just three years, upgrading by two levels with an investment of Rs 70,000 crore, whereas European companies have taken five to six years to upgrade by one level. This has meant that there was no time for local sourcing, and therefore heavy reliance on global suppliers, including China. While the collaborative planning model adopted by the industry provides a model for other sectors, the question here is, what now. In a sense, it was not just the radical change in market demand with the advent of ridesharing and e-vehicles, but also the government’s approach to policies and taxation that aggravated its difficulties.
India’s ‘Self-Goal’ in Telecom
This post was first published in the Business Standard, on March 5, 2020.
The government apparently cannot resolve the problems in telecommunications. Why? Because the authorities are trying to balance the Supreme Court order on Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR), with keeping the telecom sector healthy, while safeguarding consumer interest. These irreconcilable differences have arisen because both the United Progressive Alliance and the National Democratic Alliance governments prosecuted unreasonable claims for 15 years, despite adverse rulings! This imagined “impossible trinity” is an entirely self-created conflation.
If only the authorities focused on what they can do for India’s real needs instead of tilting at windmills, we’d fare better. Now, we are close to a collapse in communications that would impede many sectors, compound the problem of non-performing assets (NPAs), demoralise bankers, increase unemployment, and reduce investment, adding to our economic and social problems.
Is resolving the telecom crisis central to the public interest? Yes, because people need good infrastructure to use time, money, material, and mindshare effectively and efficiently, with minimal degradation of their environment, whether for productive purposes or for leisure. Systems that deliver water, sanitation, energy, transport and communications support all these activities. Nothing matches the transformation brought about by communications in India from 2004 to 2011 in our complex socio-economic terrain and demography. Its potential is still vast, limited only by our imagination and capacity for convergent action. Yet, the government’s dysfunctional approach to communications is in stark contrast to the constructive approach to make rail operations viable for private operators.
India’s interests are best served if people get the services they need for productivity and wellbeing with ease, at reasonable prices. This is why it is important for government and people to understand and work towards establishing good infrastructure.
What the Government Can Do
An absolute prerequisite is for all branches of government (legislative, executive, and judicial), the press and media, and society, to recognise that all of us must strive together to conceptualise and achieve good infrastructure. It is not “somebody else’s job”, and certainly not just the Department of Telecommunications’ (DoT’s). The latter cannot do it alone, or even take the lead, because the steps required far exceed its ambit.
Act Quickly
These actions are needed immediately:
First, annul the AGR demand using whatever legal means are available. For instance, the operators could file an appeal, and the government could settle out of court, renouncing the suit, accepting the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) ruling of 2015 on AGR.
Second, issue an appropriate ordinance that rescinds all extended claims. Follow up with the requisite legislation, working across political lines for consensus in the national interest.
Third, take action to organise and deliver communications services effectively and efficiently to as many people as possible. The following steps will help build and maintain more extensive networks with good services, reasonable prices, and more government revenues.
Enable Spectrum Usage on Feasible Terms
Wireless regulations
It is infeasible for fibre or cable to reach most people in India, compared with wireless alternatives. Realistically, the extension of connectivity beyond the nearest fibre termination point is through wireless middle-mile connections, and Wi-Fi for most last-mile links. The technology is available, and administrative decisions together with appropriate legislation can enable the use of spectrum immediately in 60GHz, 70-80GHz, and below 700MHz bands to be used by authorised operators for wireless connectivity. The first two bands are useful for high-capacity short and medium distance hops, while the third is for up to 10 km hops. The DoT can follow its own precedent set in October 2018 for 5GHz for Wi-Fi, i.e., use the US Federal Communications Commission regulations as a model.1 The one change needed is an adaptation to our circumstances that restricts their use to authorised operators for the middle-mile instead of open access, because of the spectrum payments made by operators. Policies in the public interest allowing spectrum use without auctions do not contravene Supreme Court orders.
Policies: Revenue sharing for spectrum
A second requirement is for all licensed spectrum to be paid for as a share of revenues based on usage as for licence fees, in lieu of auction payments. Legislation to this effect can ensure that spectrum for communications is either paid through revenue sharing for actual use, or is open access for all Wi-Fi bands. The restricted middle-mile use mentioned above can be charged at minimal administrative costs for management through geo-location databases to avoid interference. In the past, revenue-sharing has earned much more than up-front fees in India, and rejuvenated communications.2 There are two additional reasons for revenue sharing. One is the need to manufacture a significant proportion of equipment with Indian IPR or value-added, to not have to rely as much as we do on imports. This is critical for achieving a better balance-of-payments, and for strategic considerations. The second is to enable local talent to design and develop solutions for devices for local as well as global markets, which is denied because it is virtually impossible for them to access spectrum, no matter what the stated policies might claim.
Policies and Organisation for Infrastructure Sharing
Further, the government needs to actively facilitate shared infrastructure with policies and legislation. One way is through consortiums for network development and management, charging for usage by authorised operators. At least two consortiums that provide access for a fee, with government’s minority participation in both for security and the public interest, can ensure competition for quality and pricing. Authorised service providers could pay according to usage.
Press reports of a consortium approach to 5G where operators pay as before and the government “contributes” spectrum reflect seriously flawed thinking.3 Such extractive payments with no funds left for network development and service provision only support an illusion that genuine efforts are being made to the ill-informed, who simultaneously rejoice in the idea of free services while acclaiming high government charges (the two are obviously not compatible).
Instead of tilting at windmills that do not serve people’s needs while beggaring their prospects, commitment to our collective interests requires implementing what can be done with competence and integrity.
Shyam (no space) Ponappa at gmail dot com
1. https://dot.gov.in/sites/default/files/2018_10_29%20DCC.pdf
2. http://organizing-india.blogspot.in/2016/04/ breakthroughs- needed-for-digital-india.html
3. https://www.business-standard.com/article/economy-policy/govt-considering-spv-with-5g-sweetener-as-solution-to-telecom-crisis-120012300302_1.html
CIS Comments on 'Pre Draft' of the Report of the UN Open Ended Working Group
CIS submitted comments on the 'pre draft' report of the United Nations Open Ended Working Group on developments in the field of information and telecommunications in the context of international security.
CIS Comments on NODE Consultation Paper
CIS submitted comments in response to MEITY's Consultation Paper on National Open Digital Ecosystems (NODEs) The comments were authored by Aman Nair, Elonnai Hickok and Arindrajit Basu with inputs from Gurshabad Grover.
Announcing In Flux, the CIS Podcast
In Flux is a podcast on technology, law, policy, politics and more brought to you by the Centre for Internet and Society, India. Our episodes will explore questions around contemporary issues, and provide multidisciplinary perspectives, centred around research done by CIS. True to its name, In Flux will engage with the quickly changing and dynamic space at the intersection of technology and law. This podcast is one of our many steps to make our research more accessible to both academic and non-academic audiences.
‘Future of Work’ in India’s IT/IT-es Sector
The Centre for Internet and Society has recently undertaken research into the impact of Industry 4.0 on work in India. Industry 4.0, for the purposes of the research, is conceptualised as the technical integration of cyber physical systems (CPS) into production and logistics and the use of the ‘internet of things’ (connection between everyday objects) and services in (industrial) processes. By undertaking this research, CIS seeks to complement and contribute to the discourse and debates in India around the impact of Industry 4.0. In furtherance of the same, this report seeks to explore several key themes underpinning the impact of Industry 4.0 specifically in the IT/IT-es sector and broadly on the nature of work itself.
RBI Ban on Cryptocurrencies not backed by any data or statistics
In March 2020, the Supreme Court of India quashed the RBI order passed in 2018 that banned financial services firms from trading in virtual currency or cryptocurrency. Keeping this policy window in mind, the Centre for Internet & Society will be releasing a series of blog posts and policy briefs on cryptocurrency regulation in India

